字数 1762,阅读大约需 9 分钟
Python:Agent开发为什么使用Pydantic AI,工具篇(高级工具)
什么是pydantic ai
超级好用的AI Agent开发框架:Pydantic AI。构建人工智能驱动的应用程序往往会导致非结构化输出、类型不匹配和生产可靠性问题。将大型语言模型集成到Python应用程序中的传统方法缺乏生产系统所需的结构和验证。Pydantic AI通过将Pydantic的数据验证与用于大型语言模型交互的智能体框架相结合,解决了这一问题。

tool调用顺序
模型决定顺序:agent 使用的底层 LLM(如 GPT-4、Claude 等)会根据对话上下文和任务需求,自主决定调用哪些 tool 以及调用的顺序。
动态决策:agent 会根据:用户的问题,之前 tool 调用的结果,当前的推理状态,来动态决定下一步是否需要调用 tool,以及调用哪个 tool。
from pydantic_ai import Agent, RunContext
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4')
@agent.tool
def get_weather(ctx: RunContext[str], city: str) -> str:
return f"{city} 的天气是晴天"
@agent.tool
def book_flight(ctx: RunContext[str], destination: str) -> str:
return f"已预订飞往 {destination} 的航班"
# 用户问题:我想去北京旅游
# 模型可能会:
# 1. 先调用 get_weather("北京") 查看天气
# 2. 再调用 book_flight("北京") 预订航班
# 顺序由模型根据上下文判断优化控制执行流程
1. 通过 tool 描述引导:在 tool 的 docstring 中明确说明使用场景
2. 使用系统提示:在 agent 的 system prompt 中指定处理逻辑
3. 依赖关系设计:让某个 tool 的输出成为另一个 tool 的必需输入
4. 在 tool 内部编排:将多个操作封装在一个 tool 内部,自行控制顺序
工具输出
工具可以返回任何 Pydantic 能序列化为 JSON 的内容,也可以是音频、视频、图像或文档内容,具体取决于模型支持的多模态输入类型
from datetime import datetime
from pydantic import BaseModel
from pydantic_ai import Agent, DocumentUrl, ImageUrl
from pydantic_ai.models.openai import OpenAIResponsesModel
class User(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
agent = Agent(model=OpenAIResponsesModel('gpt-4o'))
@agent.tool_plain
def get_current_time() -> datetime:
return datetime.now()
@agent.tool_plain
def get_user() -> User:
return User(name='John', age=30)
@agent.tool_plain
def get_company_logo() -> ImageUrl:
return ImageUrl(url='https://iili.io/3Hs4FMg.png')
@agent.tool_plain
def get_document() -> DocumentUrl:
return DocumentUrl(url='https://www.w3.org/WAI/ER/tests/xhtml/testfiles/resources/pdf/dummy.pdf')
result = agent.run_sync('What time is it?')
print(result.output)
#> The current time is 10:45 PM on April 17, 2025.
result = agent.run_sync('What is the user name?')
print(result.output)
#> The user's name is John.
result = agent.run_sync('What is the company name in the logo?')
print(result.output)
#> The company name in the logo is "Pydantic."
result = agent.run_sync('What is the main content of the document?')
print(result.output)
#> The document contains just the text "Dummy PDF file."工具返回控制:ToolReturn
更精细地控制工具返回值和发送给模型的内容:
1. 为模型提供丰富的多模态内容(图像、文档等)作为上下文
2. 将程序化的返回值与模型的上下文分离开
3. 包含不应发送给大语言模型(LLM)的额外元数据
import time
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.messages import ToolReturn, BinaryContent
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o')
@agent.tool_plain
def click_and_capture(x: int, y: int) -> ToolReturn:
"""Click at coordinates and show before/after screenshots."""
# Take screenshot before action
before_screenshot = capture_screen()
# Perform click operation
perform_click(x, y)
time.sleep(0.5) # Wait for UI to update
# Take screenshot after action
after_screenshot = capture_screen()
return ToolReturn(
return_value=f"Successfully clicked at ({x}, {y})",
content=[
f"Clicked at coordinates ({x}, {y}). Here's the comparison:",
"Before:",
BinaryContent(data=before_screenshot, media_type="image/png"),
"After:",
BinaryContent(data=after_screenshot, media_type="image/png"),
"Please analyze the changes and suggest next steps."
],
metadata={
"coordinates": {"x": x, "y": y},
"action_type": "click_and_capture",
"timestamp": time.time()
}
)
# The model receives the rich visual content for analysis
# while your application can access the structured return_value and metadata
result = agent.run_sync("Click on the submit button and tell me what happened")
print(result.output)
# The model can analyze the screenshots and provide detailed feedback1. return_value:工具响应中使用的实际返回值。这部分内容会被序列化并作为工具结果发送回模型。
2. content:一系列为模型提供额外上下文的内容(文本、图像、文档等)。这会作为一条独立的用户消息出现。
3. metadata:可选的元数据,您的应用程序可以访问,但不会发送给大语言模型(LLM)。可用于日志记录、调试或其他额外处理。一些其他的 AI 框架称此功能为“artifacts”(工件)。
自定义工具
将函数转为智能体可以调用的工具
from pydantic_ai import Agent, Tool
from pydantic_ai.models.test import TestModel
def foobar(**kwargs) -> str:
return kwargs['a'] + kwargs['b']
tool = Tool.from_schema(
function=foobar,
name='sum',
description='Sum two numbers.',
json_schema={
'additionalProperties': False,
'properties': {
'a': {'description': 'the first number', 'type': 'integer'},
'b': {'description': 'the second number', 'type': 'integer'},
},
'required': ['a', 'b'],
'type': 'object',
},
takes_ctx=False,
)
test_model = TestModel()
agent = Agent(test_model, tools=[tool])
result = agent.run_sync('testing...')
print(result.output)
#> {"sum":0}动态工具
用于自定义传递给模型的工具定义,或者在该步骤中完全省略该工具:
@agent.tool 装饰器
@agent.tool_plain 装饰器
Tool 数据类
from pydantic_ai import Agent, RunContext, ToolDefinition
agent = Agent('test')
async def only_if_42(
ctx: RunContext[int], tool_def: ToolDefinition
) -> ToolDefinition | None:
if ctx.deps == 42:
return tool_def
@agent.tool(prepare=only_if_42)
def hitchhiker(ctx: RunContext[int], answer: str) -> str:
return f'{ctx.deps} {answer}'
result = agent.run_sync('testing...', deps=41)
print(result.output)
#> success (no tool calls)
result = agent.run_sync('testing...', deps=42)
print(result.output)
#> {"hitchhiker":"42 a"}智能体级别的动态工具
高级工具功能 - Pydantic AI 框架[1]
工具重试
当一个工具被执行时,其参数(由 LLM 提供)首先会使用 Pydantic 对照函数签名进行验证。如果验证失败(例如,由于类型不正确或缺少必需参数),会抛出 ValidationError,框架会自动生成一个包含验证详情的 RetryPromptPart。这个提示会发送回 LLM,告知其错误,并允许它修正参数后重试工具调用。
除了自动的验证错误外,工具自身的内部逻辑也可以通过抛出 ModelRetry 异常来明确请求重试。这对于参数在技术上有效,但在执行过程中出现问题(如瞬时网络错误,或工具判断初次尝试需要修改)的情况很有用。
from pydantic_ai import ModelRetry
def my_flaky_tool(query: str) -> str:
if query == 'bad':
# Tell the LLM the query was bad and it should try again
raise ModelRetry("The query 'bad' is not allowed. Please provide a different query.")
# ... process query ...
return 'Success!'工具并行调用
当一个模型在一次响应中返回多个工具调用时,Pydantic AI 会使用 asyncio.create_task 来并发调度它们。
彩蛋结尾
嘿,别滑了!手指停一停,听我说句悄悄话👇
🌟 关注我:下次更新,系统会自动弹窗提醒你,就像外卖到了那样准时!再也不怕错过我的脑洞和干货啦~
📌 收藏本文:这篇宝藏文章,现在不码住,以后想找只能捶胸顿足!点个收藏,让它成为你的私人知识库,随时回来挖宝~
❤️ 点赞在看:如果逗笑你了或者对你有用,麻烦高抬贵手点个赞!你的每个赞都是我熬夜写文的“鸡血”,让我更有动力产出更多有趣内容~
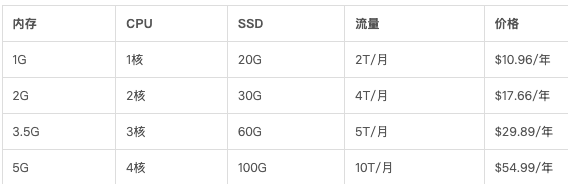
轻量云主机

专属优惠地址[2]:https://my.racknerd.com/aff.php?aff=14942
在线文档
邀请码:Zeus邀请你加入语雀,注册后在会员信息页填写邀请码 RD2QGU 即可领取 30 天语雀会员。前往注册:https://www.yuque.com/about
引用链接
[1] 高级工具功能 - Pydantic AI 框架: https://ai.pydantic.org.cn/tools-advanced/#tool-prepare[2] 专属优惠地址: https://my.racknerd.com/aff.php?aff=14942



评论区